Managed load balancing is a service offered by SolaDrive to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers. The aim is to ensure high availability and performance of applications by spreading the workload evenly across multiple resources.
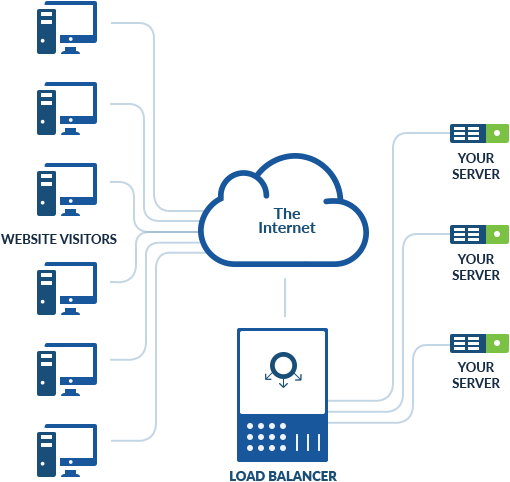
The service is typically managed by SolaDrive, freeing the customer from the responsibility of setting up, configuring, and maintaining the load-balancing infrastructure. This can include features such as automatic scaling, traffic routing based on criteria such as geography or IP address, and health monitoring of backend servers.
Importance of security in today's digital landscape
Security is a critical aspect of load balancing as it helps protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access, hacking attempts, and other cyber threats. Load balancers act as a gateway to applications and services, making them a prime target for attackers.
To ensure the security of load-balanced systems, managed load-balancing services typically offer features such as SSL/TLS offloading, IP address filtering, and application-level firewalls. These features help to secure the communication between clients and servers, and between load balancers and back-end servers.
Additionally, managed load balancing services often have built-in security features such as DDoS protection and intrusion detection & prevention systems to defend against malicious attacks. Regular security updates and patches to the load-balancing infrastructure can also help ensure the protection of sensitive data and systems.
In summary, incorporating security into the design and implementation of load balancing is crucial to protecting applications, data, and infrastructure from potential security threats.
Understanding the security challenges in load balancing
Load balancing systems can be vulnerable to a range of security threats and vulnerabilities, including:
-
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: In these attacks, an attacker intercepts and modifies the traffic between clients and servers, potentially stealing sensitive data or altering the intended communication.
-
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: Load balancing systems can be a target for DDoS attacks, in which an attacker sends a large volume of traffic to overload the system and render it unavailable.
-
SSL/TLS vulnerabilities: Load balancing systems may be vulnerable to SSL/TLS certificate-related attacks, such as impersonating a legitimate website through a mis-issued certificate.
-
Configuration weaknesses: Load balancing systems may have configuration weaknesses that can be exploited by attackers, such as weak passwords or incorrect firewall rules.
-
Backend server attacks: If a backend server is compromised, an attacker can potentially gain access to sensitive data through the load-balancing system.
-
Session hijacking: An attacker can potentially hijack a session by intercepting and reusing session tokens or cookies.
To mitigate these security threats, managed load balancing services typically provide features such as SSL/TLS offloading, IP filtering, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and regular security updates and patches. Implementing best practices for load balancing, such as using secure protocols and encryption, can also help to reduce the risk of security breaches.
Security breaches and attacks on load-balancing systems can have far-reaching impacts, including:
-
Traffic interception: Attackers can potentially intercept and modify traffic flowing through the load balancing system, potentially stealing sensitive information or altering communications.
-
Service disruption: Load balancing systems are crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of applications and services, and a security breach or attack can disrupt or take down these services, leading to significant downtime.
-
Loss of credibility: A security breach can damage the credibility and reputation of the load balancing provider and the organizations that use their services, potentially leading to lost customers and reduced trust.
-
Compliance violations: Load balancing systems used by organizations in regulated industries, such as healthcare and finance, may be subject to strict security requirements, and a security breach can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
-
Financial loss: The costs associated with a security breach can include the cost of recovery, lost revenue, and legal fees, among others.
In conclusion, the consequences of security breaches and attacks on load-balancing systems can be severe, and it's crucial for organizations to implement strong security measures and regularly assess and update their load-balancing systems to reduce the risk of breaches and ensure the continued security and reliability of their applications and services.
Features of managed load balancing services for improved security
Our managed load balancing services typically offer a range of security-related features to help protect against security threats and vulnerabilities, including:
-
SSL/TLS offloading: SSL/TLS offloading refers to the process of decryption and encryption of SSL/TLS traffic at the load balancer, rather than at each individual backend server. This feature can help to improve performance and reduce the risk of security breaches by reducing the number of SSL/TLS-related components.
-
DDoS protection: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are a type of cyberattack in which an attacker sends a large volume of traffic to a target system to overload it and render it unavailable. Managed load balancing services often provide DDoS protection features to defend against these attacks, such as traffic filtering and rate limiting.
-
Access control: Access control refers to the process of controlling who can access a system and what they can do once they have access. Managed load balancing services often offer access control features such as IP filtering, which allows administrators to restrict access to specific IP addresses, and application-level firewalls, which allow administrators to define rules for incoming traffic.
-
Encryption: Encryption helps to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access by encoding it so that it can only be decrypted with the proper key. Managed load balancing services often provide encryption features such as SSL/TLS encryption for secure communication between clients and servers.
-
Intrusion detection and prevention: Intrusion detection and prevention refer to the processes of detecting and stopping unauthorized access or attempts to modify a system. Managed load balancing services often offer intrusion detection and prevention features, such as network-level firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to help detect and prevent attacks.
These security-related features can help to protect sensitive data, applications, and systems from a range of security threats and vulnerabilities, making them an important consideration for organizations implementing load-balancing solutions.
Best practices for securing your load balancing system with managed services
Securing a load-balancing system with managed services requires a combination of technical measures and good security practices. Some best practices include:
-
Regular software updates: Keep the load-balancing software and associated systems up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates to reduce the risk of vulnerabilities.
-
Logging and monitoring: Implement logging and monitoring systems to track the activity on the load balancing system, identify security breaches and anomalies, and respond to security incidents.
-
Security audits: Regularly perform security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and assess the security of the load-balancing system.
-
Employee training: Educate employees on the importance of security and the best practices for securing load-balancing systems, including the importance of strong passwords and proper access controls.
-
Disaster recovery planning: Develop and implement a disaster recovery plan to ensure that critical systems and data can be recovered quickly in the event of a security breach or disaster.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can help to reduce the risk of security breaches and attacks and protect their load-balancing systems, applications, and data.
Having a comprehensive security strategy in place is critical for protecting organizations from a range of security threats and vulnerabilities. A well-designed security strategy should address all aspects of security, including network security, application security, and data security, and should be regularly reviewed and updated to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Our managed load balancing services play a critical role in your organization's comprehensive security strategy by providing a range of security-related features and capabilities that can help to protect against security threats and vulnerabilities.
In addition to these technical measures, our managed load-balancing services can provide valuable security expertise and best practices that can help your organization to improve its overall security posture. This can include guidance on security-related policies and procedures, threat intelligence and incident response, and regular security assessments and audits.
Ultimately, the role of our managed load-balancing services in a comprehensive security strategy is to help organizations to protect their applications, systems, and data from a range of security threats and vulnerabilities. By partnering with SolaDrive, organizations can benefit from a comprehensive security solution that combines technical security measures with expert guidance and support.
Please see our managed load-balancing offerings and service plans here.



















